迪威国际厅客服
Phone:+86 19937901373
Tel:+86-0379-65160607
Email:sophia@adahealthy.com

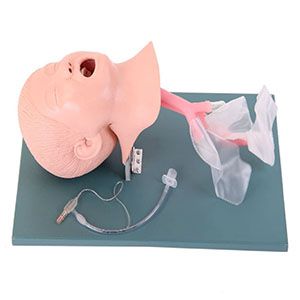
It plays a vital role in the field of medical education and training, which is not only an important tool to improve the professional skills of medical staff, but also the key to ensuring the safety of children's patients. Through highly simulated design and advanced technical support, this model provides a training platform close to actual combat for medical personnel, helping them achieve a qualitative leap in skills.

First, the airway structure and physiological characteristics of children were simulated. Children's airways are narrower and more fragile than those of adults, requiring great precision and skill during intubation. Through fine design and production, the model perfectly restores the anatomical characteristics of children's airways, so that medical staff can feel the challenge and difficulty similar to real operation during training. This highly simulated training environment helps the medical staff adapt more quickly to the complex situations in the real work, improving the success rate and safety of intubation.
Secondly, it has rich training functions and evaluation system. It can not only simulate airway conditions under different conditions, such as airway stenosis, increased secretion, etc., but also monitor the operation process of medical staff in real time, including key parameters such as intubation depth, Angle, and strength. Through immediate feedback and data analysis, the model can objectively assess the operational skill level of the medical staff and provide them with personalized training recommendations and improvement directions. This intelligent training method helps the medical staff to quickly find and correct the shortcomings in the operation, and realize the precise improvement of skills.
In addition, senior endotracheal intubation in children model has the characteristics of the reusable. Medical staff can train repeatedly at different times and in different scenarios, and deepen their understanding and mastery of tracheal intubation technology through continuous practice and exploration. This repeatable training method not only improves the efficiency and effect of training, but also reduces the training cost and time cost.
In summary, the advanced children's tracheal intubation model plays an irreplaceable role in helping medical staff to upgrade their skills. Through its highly simulated design, rich training functions and evaluation system, and reusable characteristics, it provides a safe, efficient and practical learning platform for medical personnel. On this platform, medical staff can continuously hone their skills, improve their ability to cope with complex situations, and protect the life safety of children patients.