迪威国际厅客服
Phone:+86 19937901373
Tel:+86-0379-65160607
Email:sophia@adahealthy.com

Article tag: Foot acupuncture model training model of acupuncture
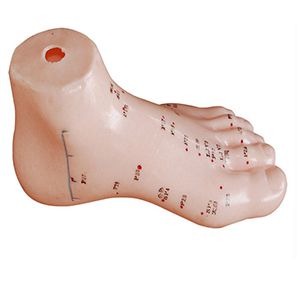
Acupuncture, as an important part of traditional Chinese medicine, plays an indispensable role in the medical field with its unique curative effect. However, it takes a long period of study and practice to become a skilled acupuncturist. In this process, the foot acupuncture model, as an important teaching tool, with its unique advantages, helps acupuncturists take a solid step on the road of professional growth.
Foot acupuncture model provides an intuitive and vivid learning platform for acupuncturists because it accurately simulates the real foot structure. Through the identification and positioning on the model, the acupuncturist can clearly see the location and distribution of the various points on the foot and the association with other meridians. This intuitive presentation allows acupuncturists to have a deeper understanding of the direction of foot meridians and the function of acupuncture points, so as to locate and operate more accurately in actual operation.
In addition to its intuitive presentation, the foot acupuncture model is highly interactive. Acupuncturists can perform repeated acupuncture exercises on the model, and get familiar with and master various acupuncture techniques and techniques by simulating real scenes. This interactive way of learning allows acupuncturists to identify and solve problems in practice, thereby continuously improving their skills.
In addition, the foot acupuncture model also has the characteristics of safety and controllability. In practice, acupuncturists are often wary of causing damage to patients. The foot acupuncture model completely eliminates this concern, providing a safe, controlled practice environment in which acupuncturists can experiment and explore without actual patients. This risk-free practice environment allows acupuncturists to operate with more confidence, thereby improving their skill level more quickly.
To sum up, the foot acupuncture model provides a valuable learning and practice platform for acupuncturists with its precise simulation, highly interactive and safe and controllable characteristics. On this platform, acupuncturists can continuously improve their skill level and gradually grow into a skilled acupuncturist. Therefore, in the future acupuncture education, we should give full play to the role of foot acupuncture model to provide strong support for the professional growth of acupuncturists.