迪威国际厅客服
Phone:+86 19937901373
Tel:+86-0379-65160607
Email:sophia@adahealthy.com

Article tag: Infantile catheterization model medical pediatric model
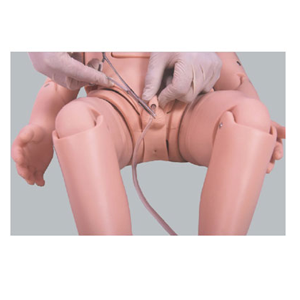
In the wide field of medical education, pediatric catheterization model, as a highly simulated teaching tool, is increasingly highlighting its core position in the training of clinical skills. This model not only provides a safe and risk-free practice platform for medical students, but also an important bridge for them to move from theory to practice and from classroom to clinical practice.

Clinical skills are essential basic skills for every medical staff, and for pediatricians, mastering the technology of pediatric urinary catheterization is crucial. Due to the significant differences between the physiological characteristics of pediatric patients and adults, the catheterization operation is more complex and delicate, requiring the operator to have high professional skills and rich practical experience. However, in the real clinical environment, due to the vulnerability of children and the high sensitivity of parents, it is often difficult for beginners to get enough practical opportunities.
At this time, the child catheterization model has become the key to solve this problem. The model accurately simulates the anatomical structure and physiological function of the urinary system in children, providing learners with an operating environment very similar to that of real patients. In this environment, learners can practice the catheterization operation repeatedly, so as to become proficient in the various steps and techniques. At the same time, due to the safety of the model, learners do not need to worry about causing harm to the child or causing medical disputes, so they can practice more confidently.
More importantly, the pediatric catheterization model also focuses on cultivating learners' clinical thinking and decision-making ability. In the simulation operation, learners need to comprehensively consider the age, illness, position and other factors of the children to develop appropriate operation plans. This comprehensive training not only helps to improve learners' operational skills, but also enables them to learn how to analyze and solve problems in practice, laying a solid foundation for future clinical work.
In addition, the infantile catheterization model is cost-effective. Compared to real clinical practice, the model is less costly to use, less risky, and can be used repeatedly. This gives more learners the opportunity to be exposed to this important clinical skill, thus promoting the popularization and quality of medical education.
To sum up, pediatric catheterization model is undoubtedly a key part of clinical skill training. With its unique advantages, it has injected new vitality into medical education and provided strong support for training more excellent pediatric medical staff.