迪威国际厅客服
Phone:+86 19937901373
Tel:+86-0379-65160607
Email:sophia@adahealthy.com

Article tag: foot joint model,joint model
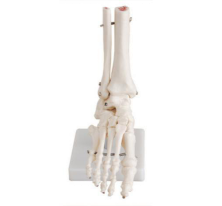
In clinical practice, foot joint models play a vital role, not only as teaching AIDS, but also as an important medium for improving clinical skills, optimizing treatment options and improving patient understanding. The following is the specific role of the foot joint model in clinical practice

1. Teaching and training
As a teaching tool, the foot joint model can help students and young doctors better understand the complex structure of the human foot joint. By observing and manipulating the model, they can visually understand the components of the foot joint such as bones, articular surfaces, ligaments, and muscles, and how these structures work together to achieve the motor function of the foot. This intuitive teaching method helps to deepen memory and improve learning efficiency
2. Skills improvement
In clinical skills training, the foot joint model provides a platform for doctors to simulate real surgery and treatment. Doctors can perform surgical simulation, manual reduction, joint puncture and other operational exercises on the model, so as to improve the accuracy of surgical skills and treatment. In addition, the model can also be used to train doctors in emergency handling capabilities in specific situations, such as dealing with emergencies such as foot fractures and dislocations
Iii. Patient education
Foot joint models can also be used for patient education. Doctors can use the model to show patients the pathogenesis and treatment of foot diseases, helping patients better understand their condition and treatment options. This intuitive educational approach helps to alleviate patients' anxiety and improve patients' treatment compliance and satisfaction
To sum up, foot joint models play multiple roles in clinical practice. They are not only a helpful assistant for teaching and training, but also an important tool for improving clinical skills and optimizing treatment plans. With the continuous development of medical technology, foot joint model will play a more important role in clinical practice.