迪威国际厅客服
Phone:+86 19937901373
Tel:+86-0379-65160607
Email:sophia@adahealthy.com

Article tag: Venipuncture model medical puncture model
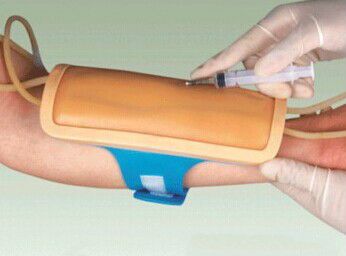
Forearm venipuncture jacket is widely used in many scenarios in medical education and clinical practice, and its high degree of simulation and practicality makes it an indispensable training tool for medical personnel. The following will elaborate on the main scenarios of its application:

1. Teaching in medical schools and nursing schools
Forearm venipunction coats play a crucial role in the teaching of medical schools and nursing schools. It provides a safe, risk-free practice platform for students to practice venipuncture in a simulated real environment. Through repeated operation and training, students can master the skills and procedures of venipuncture and lay a solid foundation for future clinical practice.
2. Clinical nursing practice
In the stage of clinical nursing practice, nurses need to master various clinical nursing skills, among which venipunction is an essential one. The forearm venipuncture jacket provides an excellent training opportunity for student nurses because of the risks and uncertainties that may be present in the actual practice. They can perform repeated puncture exercises on the model, gradually improve their operational skills and levels, and make full preparations for future clinical nursing work.
3. Skill improvement and assessment of medical staff
For already working medical staff, forearm venipuncesis jacket is also of important application value. With the continuous development and update of medical technology, healthcare professionals need to constantly learn and upgrade their professional skills. By using the forearm venipuncture jacket for simulation training, medical staff can better understand the skills and key points of venipuncture, and master the latest operating methods and procedures. At the same time, hospitals or medical institutions can also use forearm venipentesis jackets to assess and evaluate the skills of medical staff to ensure that they have sufficient clinical operation ability and level.
4. First aid training and simulation exercise
Forearm venipentesis jacket also plays an important role in first aid training and simulation exercises. By simulating the real emergency scene and patient situation, medical staff can quickly master the skills and methods of venipentesis in a short time, and improve their emergency handling ability. This type of training can not only help medical staff better respond to various emergencies, but also improve their teamwork and communication skills.
To sum up, forearm venipuncture jacket has a wide range of application values in multiple scenarios of medical education and clinical practice. It can not only improve the professional skills and level of medical staff, but also ensure the safety and comfort of patients. Therefore, we should fully realize the importance of forearm venipuncture jacket and give full play to its role in practical application.